...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
This tutorial assumes you're starting with a printed circuit board design in Eagle, and that you have access to Adobe Illustrator. |
Step 1: Obtain the Eagle .brd file
You can either follow along with your own .brd file, or use the one provided. This tutorial will be based on the open-source design file for Intan's 16-channel headstage based on the RHD2132 chip: RHD2132_headstage_16.brd
Step 2: Export a .dxf
NOTE: If you want to skip this step, you can download RHD2132_headstage_16.dxf
...
Finally, click the "User language program" button and select "dxf.ulp". Check that the default settings look fine, and click "OK."
Step 3: Process the various layers in Illustrator
- Outline
- Ensure only the bottom layer (20) is visible
- Select all (cmd/ctrl-A) and Join (cmd/ctrl-J)
- Change the Stroke to black, 0.25; change the Fill to a nice vertical gradient
...
It should now look like this:
Holes
- Lock the visible layers, and make the Holes (17) and Vias (18) layers visible
- Select all (cmd/ctrl-A)
- Set the stroke size to 0.25 mm, the Fill to white, and the Stroke to light gray
...
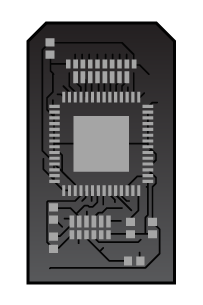
Here's the final PCB design:
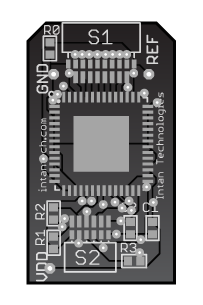
Step 4: Add surface-mount and through-hole components
This step is more subjective, and may require some amount of artistic license. Create a new layer called "Components" above the other layers, and draw your components there. If you want to copy components from an existing Illustrator file, you can use the ones in the final document: RHD2132_headstage_16.ai
This is what the board will look like once it's "populated":
Step 5: Export for the web
We like to us the "File > Export" function to generate high-quality PNGs (300 dpi or higher). Using artboards will help you keep the size of your images consistent, no matter which layers are visible.