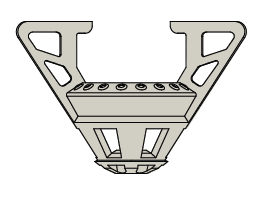
Drive body
The drive body of the flexDrive is printed from ABS like material from a CAD design file (solidworks).
There are multiple versions of the drive body - see github:flexdrive body for a full listing.
We recently added a variant that has a slightly higher EIB attachment for use with the larger 64ch eib (uses big gold pins instead of small ones). See the section on 2x32 EIBs or the github for details on the EIB.
A relatively high quality 3d print is required because otherwise the snap-fit features for the guide tubes can't be resolved and the holes for the drive screws would fill in completely. The only 3d printing method that we have tested is Stereolithography. It seems unlikely that lower-cost current generation Fused Deposition Modeling machines would give acceptable results for the flexDrive.
We are currently using APProto's Acura 55 process with very good results. Even with high print quality, drive bodies need to be prepared by drilling out and 'tapping' screw holes before using the bodies.
Close-up picture of the iner guide structure with one 33ga guide tube and a 26ga stabilizer tube.
The guide tube should easily fit into the grooves, but the stabilizer tube should not be able to slip out towards the center.